As technology evolves and the digital landscape continues to expand, cyber threats have grown exponentially. Companies are now more likely to fall victim to cyber-attacks due to the increasing sophistication of malicious software and the advent of new hacking techniques. This has resulted in a rising demand for robust cyber insurance solutions and an understanding of cyber liability.
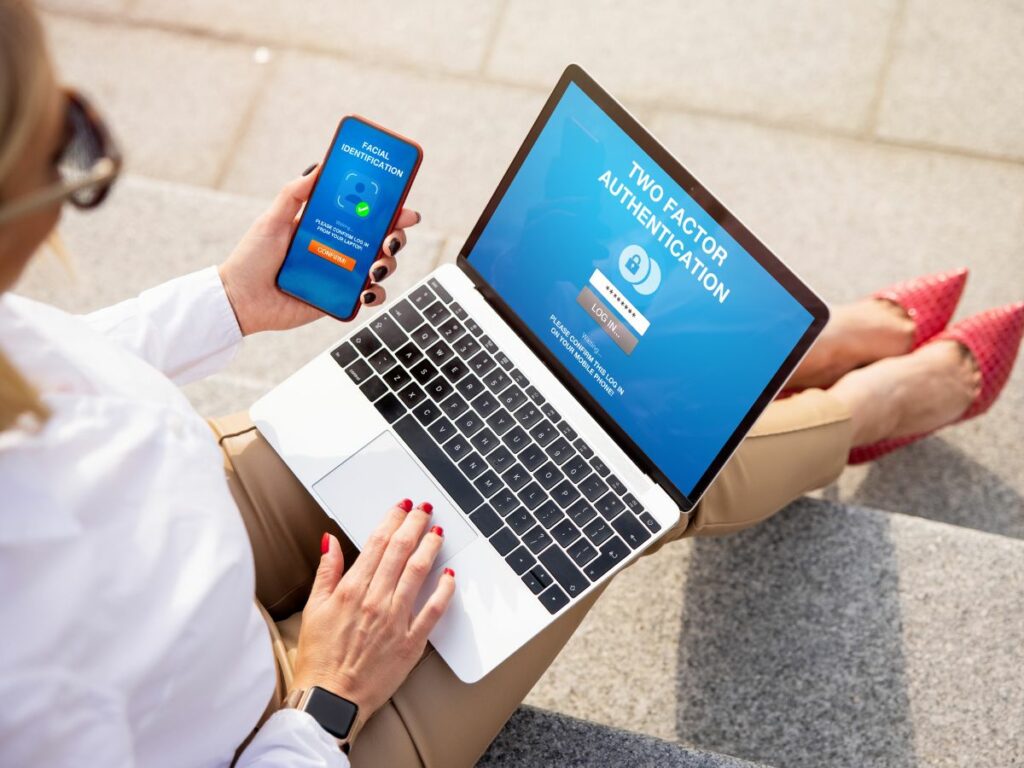
Multi-Factor Authentication Stops Cyber Criminals
The Proliferation of Cyber Crime
In 2019, the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) noted an average of nearly 1,300 complaints every day, culminating in losses exceeding $3.5 billion. Cybercriminals have developed intricate scams targeting individuals and businesses, leading to an increasing number of victims.
Cybercrimes often fund the extravagant lifestyles of the perpetrators, such as Ramon “Hushpuppi” Abbas, who flaunted his collection of designer clothes, luxury cars, and private jets.
Cybercriminals are now employing highly targeted methods like Business Email Compromise (BEC), which involves hijacking and impersonating a business email account. However, there are effective ways to block these complex attacks, and cyber insurance plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk.
How Cybercriminals Operate
In a BEC attack, an attacker hacks into a corporate email account and impersonates the real owner to defraud the company. The criminals trick customers, partners, and employees into sending money or sensitive data. The attacker might gain entry to the company’s email by targeting a lower-level employee through various methods, including brute force, credential harvesting, and phishing.
Once the attacker gains access, they can exploit the company’s information to execute their schemes. They often impersonate an executive, using an urgent request to persuade an employee to transfer a large amount of money to an account owned by the criminals.
Why Email Impersonation Succeeds
The critical factor in email-related fraud is whether the recipients believe the authenticity of the request. Such theft is possible because the transactions are real and expected. This is where the term social engineering is derived.
Cybercriminals bank on socially reinforced patterns. A well-known BEC scam redirected invoice payments totaling $75 million to cybercriminal bank accounts. Despite the vast amount of money involved, nobody noticed.
The Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication
Since passwords account for 80 percent of hacking-related breaches, other layers of protection are needed to prevent cybercrime losses. One effective method is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), offering a second line of defense against email account hijacking and related BEC cybercrime.
How MFA Works
MFA requires two or more authenticating factors to ensure access to company email and other key company assets are restricted to authorized personnel. The authenticating strategy behind MFA involves up to three layers of protection:
- Something you know (typically a password or verification code)
- Something you have (a trusted device that is not easily duplicated)
- Something you are (biometrics)
Implementing MFA
Enabling MFA can be one of the quickest and most impactful ways to protect user identities. Even after MFA is enabled, organizations should ensure that vendors, suppliers, business partners, and customers interacting with their computer networks also enable MFA.
The Vital Role of Cyber Insurance and Understanding Cyber Liability
As the risk of cybercrime continues to escalate, it’s more important than ever for businesses to understand the value of cyber insurance and the implications of cyber liability. Cyber insurance can provide a financial safety net for businesses, covering losses related to cybercrime. Cyber liability refers to the legal responsibility a company has in the event of a data breach where customer information is stolen.
How Cyber Insurance Works
Cyber insurance policies are designed to cover a variety of risks. These may include costs associated with data breaches, such as legal fees, public relations efforts, notification costs, and credit monitoring services. Policies may also cover losses resulting from business interruption, data loss recovery, and cyber extortion.
Understanding Cyber Liability
Cyber liability refers to a company’s responsibility in the event of a data breach in which sensitive customer information is exposed. This could include anything from credit card numbers to personal health information. If a company is found to be negligent in protecting this data, they may be held liable for the breach.
Cyber Insurance in Action
A robust cyber insurance policy can provide coverage for a wide range of scenarios. For example, if a business falls victim to a BEC scam, resulting in significant financial loss, a cyber insurance policy could potentially cover the loss.
Conclusion
In today’s digital age, a comprehensive understanding of cyber insurance and cyber liability is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Protecting against cyber threats involves a multi-faceted approach, including advanced security measures like MFA and robust cyber insurance policies. By taking a proactive approach to cyber security, businesses can safeguard their assets, protect their customers, and maintain their reputation in the face of emerging cyber threats.